
European Commission, 2023
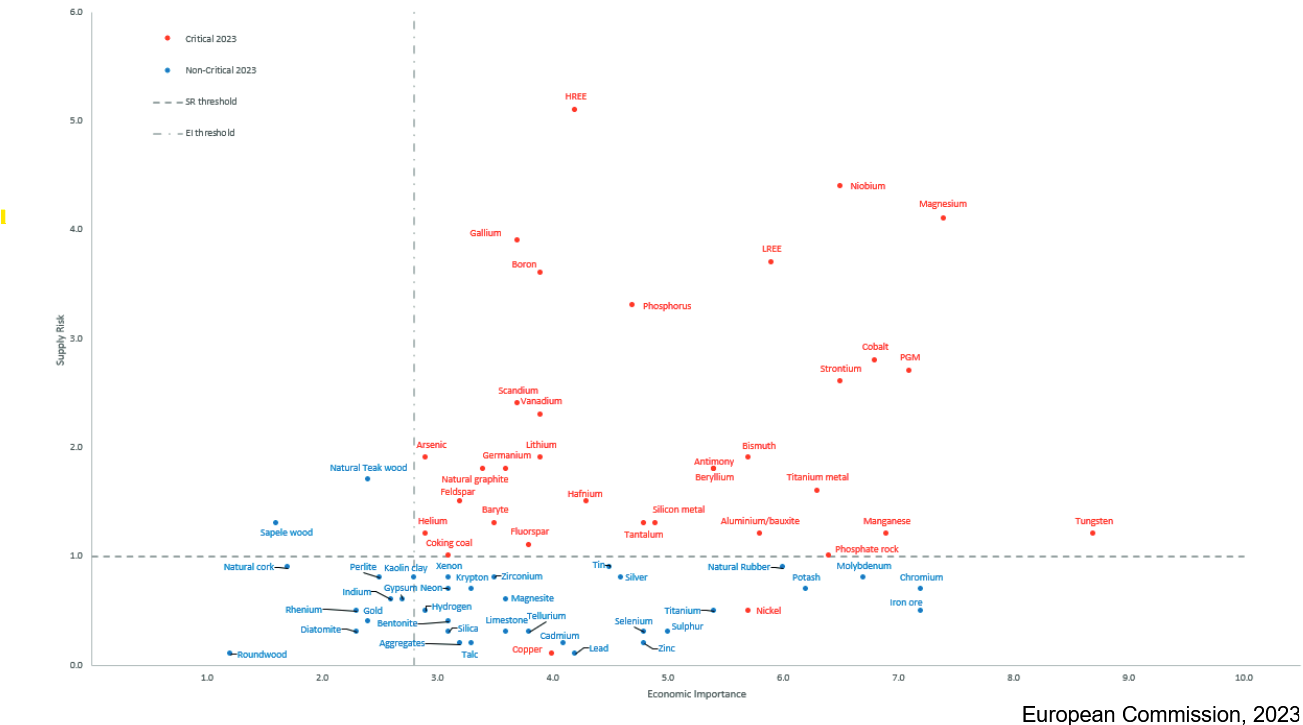
Critical raw materials (CRM) are defined by the European Commission as raw materials that play a crucial role in the European Union's economy and whose supply is associated with a high risk. To assess the criticality of a material, the European Commission relies on two indicators:
- The supply risk (SR) defined as 'reflecting the risk of disruption in the EU's supply of the material. It is based on the concentration of primary supply from raw material producing countries, considering their governance performance and commercial aspects
- The economic importance (EI) defined as the importance of a material to the EU economy in terms of final applications and the added value it brings to the EU's manufacturing sectors at the NACE rev.2 level (European statistical classification of economic activities)
The graph opposite positions critical materials in relation to their economic importance (EI) and supply risk (SR). The CRM with the highest criticality are therefore placed at the top right, and include the Light Rare Earth Elements (LREE), Niobium, and Magnesium.
CRRISP provides an additional element of analysis to the two previously mentioned: the annual mining production of CRM.